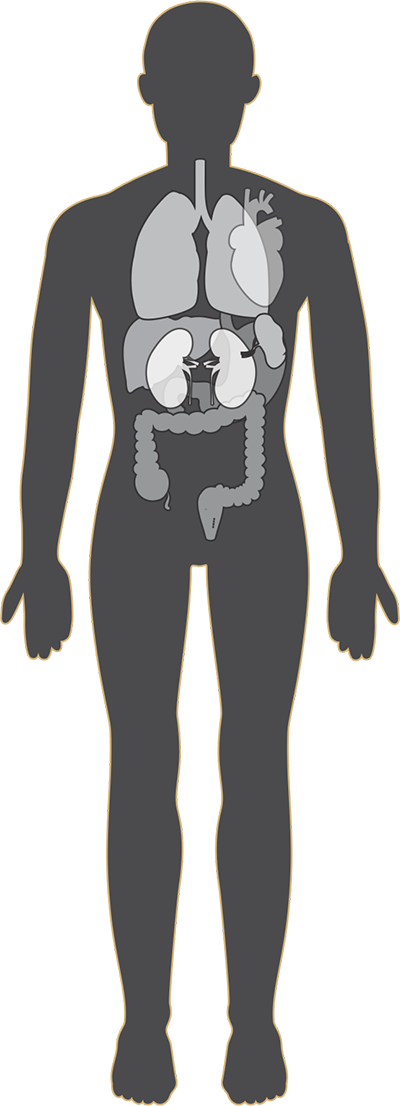
What is a general surgeon?
General surgeons are doctors who performs surgery and treat a wide spectrum of disease and injury. These Surgeons have knowledge about several important aspects of human body’s structure and functions of organs
Surgical procedures are a treatment approach to diagnose or manage a medical condition, especially if it alters the organ or tissue.
These doctors perform surgeries that help promote health, removal of diseased organs, injury repair and wound healing. In addition, they provide quality medical care before, during and after any surgical procedure
General surgeons also recommend diagnostic tests to guide on the need for surgery.
General surgeons typically require a minimum of 13 years of college, medical school and residency before they can practice
What does a general surgeon do?
A general surgeon performs surgical procedure on the diseased area present at any part of the body. The most common sites include breasts, abdomen, digestive system organs and endocrine system glands.
Types of surgery
- Open Surgery
- Minimally invasive surgery
Wound repair
- Process of blood clotting
- Importance of immune system
- Infections and antibiotics
Diagnosis & scopes
- EGD (Upper GI Endoscopy)
- Biopsy
Types of surgical admission options for General Surgeons
There various way one can receive treatment from a general surgeon
Optional or elective surgery
Elective surgery is a medical procedure that is scheduled because it does not involve a medical emergency. A Semi-elective surgery is a surgery that must be done but does not need to be performed immediately.
Required surgery
This surgical approach helps to improve quality of life in the future. For example, removal of kidney stones, if not managed by medications or lifestyle changes. Required surgery does not need to be performed immediately, unlike emergency surgery
Urgent or emergency surgery (Non elective surgery)
In an urgent medial situation the general surgeon performs this surgery. For example acute appendicitis.
Different types of surgical methods
Open surgery method
In open surgery, the surgeon is able to view the disease related structures by cutting the skin and tissues. Removal of organs such as gallbladder or appendix is an example of open surgery.
Minimally invasive surgery
This approach is a technique which does not involves large incision. The main advantage of minimally invasive surgery is that there is less pain and faster healing.
Treatment Guide
Diagnosis & scopes
A general surgeon is competent to diagnose a variety of illnesses from head to toe. They own a broad knowledge helps identify signs and symptom
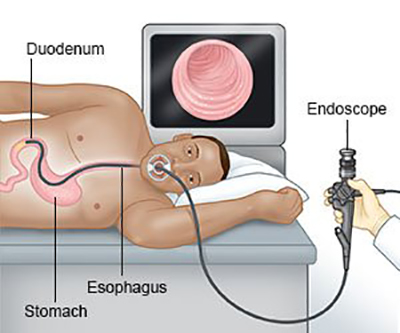
EGD (Upper GI Endoscopy)
or esophagogastroduodenoscopy, is a diagnostic procedure. Doctors use an endoscope—a thin, lighted tube with a camera on the end—to see the inside of your upper GI tract.
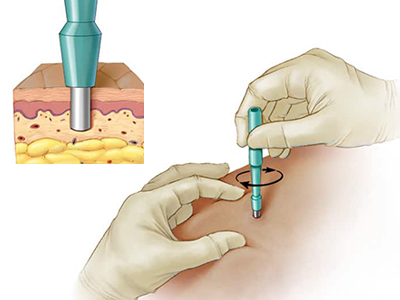
Biopsy
Biopsy is a diagnostic process that examines body tissue or fluid to check if there is presence of a suspected disease. Biopsies can help in diagnosing disease such as infections, tumors, and inflammatory conditions. Depending on the diseased site, there are several ways for removing a biopsy sample. A GS can either remove a small piece of skin/tissue
Surgical procedures performed by General Surgeon
A general surgeon has the knowledge and experience necessary to manage surgery at all stages. This includes initial evaluation, surgical preparation, performing procedure and post-operative care.

Neck
Tonsils removal
Tonsillectomy is the removal of one or both the tonsils surgically.
Total thyroidectomy
A surgical procedure that removes the thyroid gland completely. This is usually an effective approach for treating thyroid cancer, but it can also be indicated for other conditions such as goiter, and uncontrollable hyperthyroidism. Sometimes while performing thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer removal of lymph nodes is suggested by a pathologist. A small incision around the neck helps to limit scarring. Typically, the surgical process is conducted under general anaesthesia.
Thyroid lobectomy
It is a surgery that removes one of the two thyroid lobes, and keeps the other one intact. The nodules may cause symptoms demonstrating cancerous characteristics. Another use of this surgical procedure is management of excessive hormone production such as in hyperthyroidism.
Parathyroidectomy
Parathyroid glands are small, four pea-shaped glands, present on either side of the trachea within the neck, and adjacent to the thyroid gland. Most commonly, two glands are present, a superior and an inferior gland. Paarathyroidectomy is a surgery involving removal of parathyroid glands, and manages hyperparathyroidism.
Thyroid gland surgery
Excessive production of certain hormones may occur if the thyroid gland becomes overactive. Thyroid gland surgery is usually performed if cancer of thyroid is present. Based on severity of the condition, GS can either excise a certain part or entire part of thyroid. Synthetic hormones are prescribed to replace any lack of hormones.
Thyroid gland surgery
Excessive production of certain hormones may occur if the thyroid gland becomes overactive. Thyroid gland surgery is usually performed if cancer of thyroid is present. Based on severity of the condition, GS can either excise a certain part or entire part of thyroid. Synthetic hormones are prescribed to replace any lack of hormones
Breast & Chest
Breast surgery is a treatment for breast cancer. Apart from this, other reasons for performing breast surgery are:
Breast biopsy
Removal of a small breast tissue helps to check if tumor is present.
Lumpectomy
It involves removal of tumor from the breast and known as breast-conserving surgery, or partial mastectomy.
Mastectomy
One or both the breasts undergo surgical removal as a result of breast cancer, called as mastectomy.
Breast lumpectomy
This surgery removes tumor from the breast. Different names for this approach are breast-conserving surgery, wide excision and partial mastectomy.
Gynecomastia surgery
It is the surgical removal of enlarged breasts in men. Gynecomastia is a condition where men can have overdeveloped or enlarged breasts. Risk factors for this condition include genetic susceptibility, obesity or the use of certain drugs. In the surgery, reduction of breast takes place along with flattening the contours, along with chest enhancement
Mastectomy
It is a process that removes a part of breast, or the breast completely. Usually, helps for the treatment of breast cancer. Based on the degree of tumor involvement it can be of two types:
-
- Partial (segmental) mastectomy removes the cancerous tissue and a large area around the normal breast tissue.
- Total (or simple) mastectomy is a surgery that removes entire breast, including the areola (circular portion around the nipple), the nipple and overlying skin. Additionally, excision of lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph glands) is also done in some cases.
Oesophagus & Stomach
In case medications fail to manage esophageal diseases, osophageal surgeries are the next best option. It includes:
Acid reflux surgery
It helps to manage GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). Acid reflux happens when the esophageal muscles are unable to close the opening of stomach tightly. In acid reflux surgery closure of the stomach opening occurs by wrapping the upper portion of stomach around the lower part of esophagus.
Esophagectomy
Removal of esophagus is esophagectomy. A treatment approach to manage esophageal cancer and precancerous condition, Barrett’s esophagus.
Excision of an esophageal lesion:
It involves removal of any suspected lesion or growth from the esophagus by general surgeon.
Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction refers to blockage of the intestine which can either be partial or complete blockage. In a normal healthy state, the foods that undergo digestion flows and reaches the large intestine. However, if an obstruction occurs in the small bowel then the contents are unable to pass through. In such situation all the waste products accumulate above the site of blockage, and interferes with the absorption of certain key elements (such as nutrients and fluids).
Bowel obstruction most commonly occurs due to cancer of stomach, colon and ovary. The GS conducts a physical examination, and imaging tests to manage the condition
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a digestive condition that involves the large intestine. Diverticula are small pockets or bulges that may develop with age. Generally, they do not cause any harm and patient may not have any symptoms for months. During infection or any inflammatory condition these diverticula show severe symptoms resulting in diverticulitis. Research suggest that inadequate intake of fiber in the diet leads to diverticulitis and other diverticular disease.
The General surgeon assess the condition based on a thorough medical history as there are certain other medical conditions which present with similar symptoms. For example, bowel cancer, celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Spleen removal
Spleen helps to prevent infection, regulate blood clotting, and destroys damaged blood cells. Enlarged spleen will be unable to perform these functions adequately. It may result in spleen burst and internal bleeding. Hence, spleen removal is important.
Gastrointestinal / abdomen
General surgeon can perform surgeries to treat all types of gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. This includes:
Appendectomy: Surgical removal of appendix is appendectomy. Appendix is a small pouch that joins the large intestine. Appendix removal helps to cure appendicitis, an inflammation or infection of appendix. Appendectomy is useful to remove tumors from the appendix.
Appendix removal
Appendectomy: Surgical removal of appendix is appendectomy. Appendix is small pouch that joins the large intestine. Appendix removal helps to cure appendicitis, an inflammation or infection of appendix.
Gastric bypass surgery
An indication for managing obesity. The surgical approach can involve either intragastric balloon or metabolic/bariatric surgery. Overall anatomy of stomach changes due to reduction in stomach size
Hernia
Surgical correction of hernia refers to hernia repair. Basically, hernia occurs when any organ protrudes through a weakened part of muscle or tissue.
They can bulge into several structures such as thigh, groin, chest or belly button causing a lump. General surgeon helps to protrude the organ back into its original place and manage the weakened area of muscle or tissue.
Skin and Soft Tissue
- Lumps
- Cancer
- Cysts
- Abscess
- Cellulitis
Rectal Surgery & Colon
Surgery on rectal and colon is performed to manage different medical conditions such as cancer, Crohn’s disease, diverticulitis, injury, and bowel obstruction. The surgeries commonly include:
Small intestine, Colon and Rectal Surgery
Surgical procedure involving small intestine, colon and rectum provides effective results for a wide variety of conditions. This includes cancer, Crohn’s disease, bowel obstruction, haemorrhoids and diverticulitis. The most common surgeries are colectomy, colostomy, and hemorrhoidectomy.
Colectomy
A surgical procedure where part of the colon or large intestine is removed. It is also called as colon or bowel resection. Incision is made in the abdomen. In colectomy the patient spends few days in the hospital and full recovery may take several weeks.
Colostomy
It is a surgery where colon is connected to the external opening in the abdomen, known as stroma. Individuals with colostomy excrete stool through the colostomy into a special bag rather than via rectum.
Hemorrhoidectomy
It removes haemorrhoids, also known as piles. Piles are nothing but swollen, inflamed blood vessels in the rectum and anus. Lifestyle modifications help to manage this condition, however large and severe haemorrhoids require surgery.
Crohn’s disease
It is an inflammatory bowel disease, chronic in nature which targets the digestive tract lining.It usually occurs in the colon and small intestine, but it can target any part of the GI tract starting from the mouth to anus.The most common symptoms are weight loss, abdominal pain, fatigue, anemia, and diarrhoea.
This condition may cause life-threatening complications in some individuals, while in others it may remain unnoticed. GS can perform surgery to manage the condition, although surgical approach is the last resort when other interventions are unable to improve the condition.

